Case Study: Reducing the Costs of Fuel and Engine Rebuilds
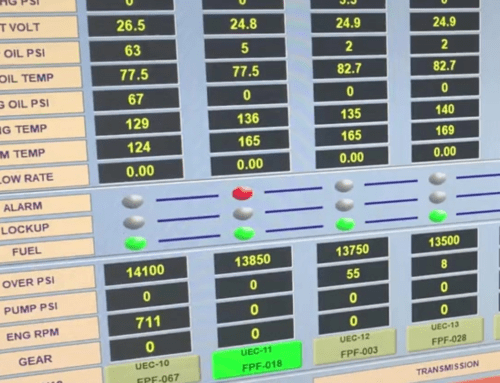
Fuel efficiency stands at the core of operational cost-effectiveness and environmental responsibility. Recognizing this, the study aimed to quantify the fuel consumption of a 2500 BHP frac pump engine during idle periods and under the strain of external loads amidst fluctuating ambient temperatures.
Solution
The methodology involved the strategic installation of fuel flow meters on a test engine, which was then rigorously analyzed on a dynamometer over an extended period. This allowed the capture of accurate fuel consumption data under varied conditions, providing a comprehensive understanding of the engine’s performance.
The analysis revealed critical insights into the fuel consumption patterns of frac pump engines:
Significant savings can be achieved through decreased fuel consumption and engine maintenance by minimizing engine idling. The MGB PowerCELL technology platform was proven in a separate study to reduce idle times by up to 85% in a typical frac operation without requiring extra capital investment. This leads to considerable cost savings while also reducing the environmental footprint.
These findings highlight a significant opportunity for operational improvement. By focusing on reducing idle times and managing operational loads more efficiently, there is a potential to achieve substantial cost savings and minimize environmental impact.